Runtime Data Collection
The Necessity of a Full-Stack Approach for Achieving
Comprehensive Security in Modern Applications
A fullstack approach
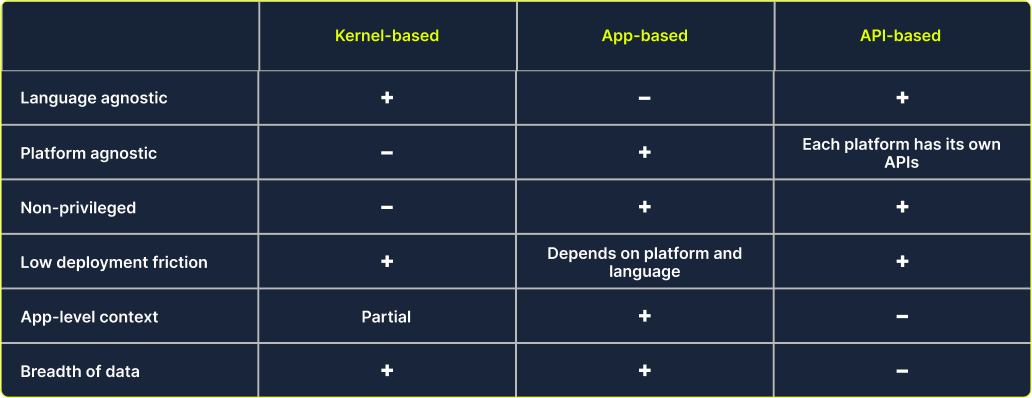
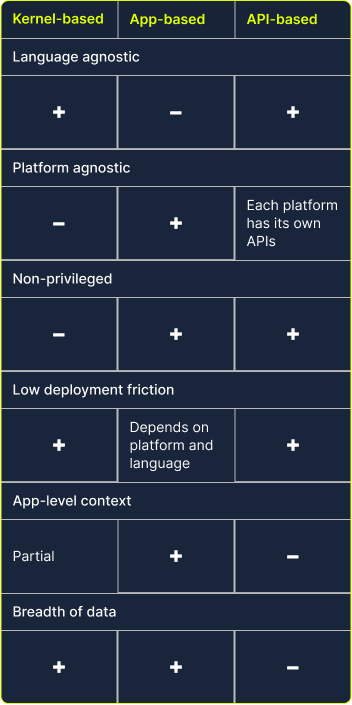
Comprehensive data collection is paramount for understanding, optimizing, and securing modern applications. There are three methodologies for runtime data collection: Kernel-based, application-based, and API-based. These techniques offer unique advantages allowing security, development, and operations teams to gain insights into various aspects of their systems. That said, each of these methods has limitations and neither one provides complete coverage on its own.
Helios combines multiple runtime data collection methods to provide context, granular data, and a comprehensive picture of the application’s security posture in runtime
Kernel-based data collection
eBPF, or Extended Berkeley Packet Filter, is a kernel technology available since Linux 4.4. It allows developers to run programs without adding additional modules or modifying the kernel source code. Think of it as a lightweight, sandboxed virtual machine within the Linux kernel that lets you hook into kernel calls and extract data in an efficient and safe way.
Use case example
Monitor incoming networking calls made by processes, allowing for the early detection of potential exploitations.
Limitations:
- Can’t be used in clusters without privilege mode – In EKS Fargate and GKE Autopilot, running a container in privileged mode, which is required for eBPF, is not allowed, because the Kubernetes nodes are managed by AWS/GCP.
- Can’t be used when there is no access to the Kernel, like Lambdas.
- Hardened environments that don’t allow running as root.
Limitations:
1: Can’t be used in clusters without privilege mode – In EKS Fargate and GKE Autopilot, running a container in privileged mode, which is required for eBPF, is not allowed, because the Kubernetes nodes are managed by AWS/GCP.
2:Can’t be used when there is no access to the Kernel, like Lambdas.
3:Hardened environments that don’t allow running as root.
Application-based data collection
App-level instrumentation encompasses various techniques across different languages and runtimes to gather data by integrating with the application, often by adding code either explicitly or implicitly. This typically involves replacing function implementations at runtime with wrapped versions that capture information about their executions, including durations and return values. Modern methods have made this process more transparent. Dynamic languages like Node.js and Python allow script loading before the main program starts, and Java’s javaagent mechanism is used for similar purposes.
Use case example
App-level instrumentation: Using eBPF as the instrumentation mechanism to gather telemetry data for distributed tracing.
Limitations:
- Errors in the instrumentation can interfere with the application.
- Not all languages support app-level instrumentation without code changes to the application.
Limitations:
1: Errors in the instrumentation can interfere with the application.
2: Not all languages support app-level instrumentation without code changes to the application.
Use case example
Extract all running Docker images from a K8s cluster
Limitations:
API-based data is limited in its nature. Runtime data is most unavailable to them (e.g., knowing if a certain package is loaded into memory or if a vulnerable function is invoked)
Limitations:
API-based data is limited in its nature. Runtime data is most unavailable to them (e.g., knowing if a certain package is loaded into memory or if a vulnerable function is invoked)
Comprehensive runtime data collection is essential for securing applications and infrastructure. While each data collection method offers unique advantages and insights into different aspects of the application, they come with inherent limitations. To address these shortcomings, a hybrid approach is crucial. Helios combines multiple data collection methods, providing context, granular data, and a holistic view of an application's security posture during runtime.
Save time with runtime
Helios is compliant with:

Menu
Save time with runtime



© Copyright 2022 – All rights reserved